For real estate investors eyeing the lucrative opportunity to house hack a three or four-family home, the FHA self-sufficiency test is designed to ensure that multi-unit properties can generate enough rental income to cover the mortgage expenses.
As an investor, before plunging into the house hacking strategy—a method where you live in one of the units of your property and rent out the others—it’s vital to ensure that your investment can pass this test.
So, as we navigate this guide, we’ll unpack how the FHA self-sufficiency test plays a significant role in shaping your house hacking ventures and why it’s crucial to have this knowledge in your real estate toolkit. Let’s dive in!
What is the Self-Sufficiency Test for FHA Loans?

The self-sufficiency test is a criterion established by the Federal Housing Administration (FHA). Its primary purpose? To gauge whether a property can produce enough rental income to cover its mortgage payments. A property is considered self-sufficient if the net rental income exceeds the mortgage expenses (principal, interest, taxes, mortgage insurance premiums, and hazard insurance).
In simpler terms, the FHA wants to ensure that if a homeowner were to rent out all units, the generated income would be sufficient to sustain the property’s mortgage obligations. This is crucial in preventing potential foreclosures and ensuring the financial stability of the lender and the borrower.
What Properties are Subject to the FHA Self-Sufficiency Test?

The FHA self-sufficiency test applies to three to four-unit properties. For these kinds of homes, the mortgage expenses can not exceed 100% of the net rental income produced by the property. Pictured below is the FHA’s self-sufficiency standard:

If you’ve got your eye on house hacking, this test is more than just a checklist item. It’s a litmus test. Next, we’ll explore how lenders calculate the rental income for the self-sufficiency test.
How do Lenders Calculate Rental Income?

Net rental income is calculated using the appraiser’s estimate of fair market rent from all units, including the owner’s unit then subtracting a vacancy and maintenance allowance of at least 25%. But, what methodologies lie at the foundation of these assessments?
Market Rent Analysis from the Property’s Appraisal
Performed as a part of the property’s appraisal, this analysis reviews comparable rental properties near the subject (your) property to determine the likely rent one can charge. By understanding these comparative figures, lenders can gauge a property’s income potential and whether it aligns with the expectations set by the FHA guidelines.
Percentage of Rental Income
Instead of considering the entire amount, lenders often use a specific percentage (typically around 75%) to account for potential vacancies and maintenance costs. This conservative approach ensures a buffer, providing both the lender and borrower with a safety net against unforeseen rental disruptions.
Understanding these calculations is pivotal if you are considering house hacking. By knowing how lenders view rental income and their criteria, you are better positioned to evaluate a property’s likelihood of being approved for FHA financing.
Let’s bring this together and go over a real-life example.
Example of an FHA Self-Sufficiency Test
Here’s a three-family home listed in Detroit, MI:

The first thing we need to do is calculate our mortgage expenses. This includes principal, interest, taxes, insurance (PITI), and mortgage insurance premiums. Let’s assume the following:
- Purchase price: $150,000
- Down payment: 3.5%
- Interest rate: 7.5%
- Annual property taxes: $1,180
- Annual insurance: $1,500
Using these variables, our PITI expenses, including mortgage insurance premiums, are equal to $1,301.79
Next, we’ll need to figure out our market rent. The property in this example consists of (3) one-bedroom apartments. So, let’s take a look at what a one-bedroom rental is going for:
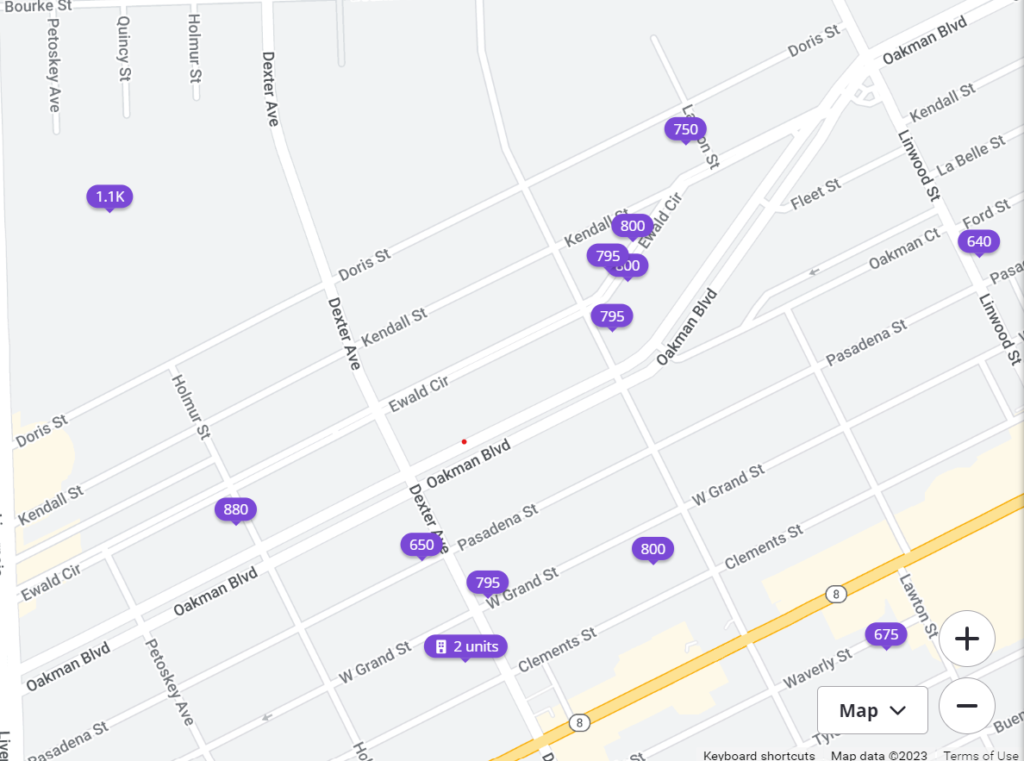
Looking at the available listings near our subject property, we will use $795 as the market rent.
- Unit 1: $795
- Unit 2: $795
- Unit 3: $795
Total: $2,385
But, we can’t just use gross rent; to calculate the Net Self-Sufficiency Rental Income, we have to apply a 25% vacancy and maintenance factor:
$2,385 x 25% = $1,788.75
We now have the following:
- Mortgage Payment: $1,301.79
- Net Self Sufficiency Rental Income: $1,788.75
To figure out if this three-family home will pass the FHA self-sufficiency test, the monthly mortgage payment divided by the monthly net rental income cannot exceed 100%:
$1,301.79 divided by $1,788.75 = 72.8%
Since the percentage is less than 100%, this listing passes the self-sufficiency test!
Next, let’s explore what you can do if your property fails the FHA self-sufficiency test.
If a Property Fails the FHA Self-Sufficiency Test, What’s Next?
Every real estate investor’s journey is unique, and only some multi-unit properties will seamlessly align with the FHA self-sufficiency test. Should a property fall short of the criteria, there are alternative avenues to explore:
Increase Your Down Payment
Increasing your down payment is one of the most direct ways to make a 3-4 unit home pass the self-sufficiency test. With a reduced loan amount, the monthly mortgage obligation drops, making it more likely for the property’s rental income to cover the mortgage, thus meeting the FHA self-sufficiency test criteria. While this approach might require a heftier initial capital outlay, it can streamline the financing process, paving the way for a successful house hacking experience.
Renegotiate the Purchase Price
Consider renegotiating the purchase price if the property’s rental income potential is slightly off from meeting the FHA guidelines. A reduced price can affect the loan calculations, allowing the property to meet the self-sufficiency criteria.
Opt for a Different Financing Option
While FHA loans are popular, especially among first-time house hackers, they aren’t the only financing method available. Although the down payment requirements are higher, conventional loans or other lending programs have different criteria, allowing investors to proceed with their desired property.
Remember, while the FHA self-sufficiency test can be a hurdle in financing, it’s not the end-all. By exploring alternatives and being open to different strategies, one can pivot effectively, ensuring that your investment vision comes to fruition.
How Do I Know If a Property is Self-Sufficient Before Offering to Buy It?
Making an offer on a multi-unit property, especially with the intention of house hacking, can be exhilarating. But before taking that step, it’s vital to ascertain if the property passes the FHA self-sufficiency test. So, how can you, as an investor, ensure that the numbers add up favorably?
Research Rental Market Rates
Much like the example we went through earlier, delving into local listings, platforms, and even neighborhood discussions can offer a window into prevailing rental rates. This proactive research aids in forming realistic rental income expectations, ensuring that the property’s income potential aligns with the FHA self-sufficiency test. While searching sites like Zillow, Redfin, and Trulia can give you a ballpark figure of what other landlords in your area seek in rent, MLS (multiple listing service) records can offer insight into what comparable units are rented for.
Engage with a Local Real Estate Agent
Collaborating with an experienced local agent can be invaluable. The right real estate professional is often well-versed in the FHA guidelines and can provide insights into the rental market’s dynamics. They can also assist in sourcing comparative rent data for similar properties, granting a clearer picture of potential rental income.
Consult with FHA-Informed Lenders
Speaking directly with lenders knowledgeable about FHA loans can be beneficial. They can provide preliminary assessments based on the property details and rental income estimates, offering a practical perspective on the property’s self-sufficiency.
Ensuring a property’s self-sufficiency upfront bolsters the chances of loan approval and solidifies the foundation for a successful house-hacking venture.
Impact on House Hacking
a. What is house hacking?
House hacking is an ingenious real estate investment strategy wherein an individual purchases a multi-unit property, resides in one of the units and rents out the remaining units. The rental income generated from the other units typically offsets the mortgage payments and sometimes even results in additional monthly cash flow.
For many, house hacking is an entry point into real estate investing, allowing them to leverage property appreciation, gain property management experience, and reduce or even eliminate housing costs.
b. How the FHA self-sufficiency test can impact house hacking:
The relationship between the FHA self-sufficiency test and house hacking is intrinsic. For many first-time owners, FHA loans offer favorable down payment terms, making diving into multi-unit property investments more feasible. However, with the self-sufficiency test in play, there are specific criteria these properties must meet.
If a 3-4 unit property doesn’t generate sufficient rental income to cover its mortgage payments, per FHA guidelines, it can become a challenge for you to house hack with an FHA loan. This can limit the range of properties you might consider, potentially excluding otherwise perfect homes that fall just shy of the test’s requirements.
On the flip side, understanding and meeting the FHA self-sufficiency test criteria ensures that the chosen property can sustain itself financially. For house hackers, this means the likelihood of successful loan approval and the assurance of a property that’s truly optimized for rental income, promising a smoother and more profitable investment journey.
The Wrap Up
Embarking on a journey into real estate, especially with strategies like house hacking in mind, demands a solid grasp of the myriad guidelines and requirements that shape the investment landscape. Central to this understanding is the FHA self-sufficiency test—a pivotal criterion determining the viability and financial sustainability of 3-4 unit properties.
This test might seem like just another box to tick for the uninitiated. However, as we’ve discovered, it’s evident that its implications are vast, influencing property choices, financing options, and the overall trajectory of an investor’s house-hacking venture.
Key Takeaways from the Article:
- The FHA self-sufficiency test ensures that multi-unit properties can generate adequate rental income to cover their mortgage obligations.
- Lenders primarily rely on market rent analysis and a percentage of current rental income to determine a property’s income potential.
- Proactive research, consulting with FHA-informed lenders, and collaborating with local real estate agents can help assess a property’s self-sufficiency before making an offer.
- If a property doesn’t pass the test, investors have alternatives like opting for different financing, renegotiating the purchase price, or seeking co-borrowers.
- Increasing the downpayment reduces the loan amount and is a direct way to make a property more self-sufficient.
- House hacking, a strategy of living in one unit and renting out the others, is deeply influenced by the FHA self-sufficiency test, highlighting the importance of this criterion for aspiring and seasoned investors alike.